
A currency pair is a tradable product made up of two currencies. Currency pairs are listed on your brokers menu so you can choose which one you want to trade.
Every currency pair product has a price tag attached to it & this price is called the exchange rate.
So whenever you want to trade, visit your brokers menu & select a currency pair you can afford based on your account balance.
X-Ray of a Currency Pair

The currency on the left-hand side of the pair is called the Base Currency, while that on the right is the Quote Currency.
The exchange rate of any currency pair is the amount of the quote currency you need to buy 1 unit of the base currency.
So, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.0694, then it will take 1.0694 USD to buy 1 EUR. The exchange rate is always expressed in the quote currency.
Usually exchange rates for currency pairs are quoted to 4 decimal places but when there’s a need for more precision, exchange rates can be quoted to 5 decimal places (5-digit pricing as brokers like to call it).
Your forex broker is the one to pair the currencies together then you select the one you desire.
Not all currency pairs are the same. Some are highly sought after (high liquidity) and some are sparsely traded (low liquidity).
Types of Currency Pairs
- ✅Major currency pairs (highly sought after & very popular)
- ✅Minor currency pairs
- ✅Exotic currency pairs
What are the 7 Major Currency Pairs?
A major currency pair consists of the US Dollar plus the currency of another economic superpower country. There are 7 major currency pairs in the forex market. See table below:
| 🗺️Economy | 🗺️Economy | 💱Currency pair | 🪪Type | 🪪Nickname |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | USA | EUR/USD | Major | Fiber |
| Great Britain | USA | GBP/USD | Major | Cable |
| USA | Japan | USD/JPY | Major | Gopher |
| USA | Switzerland | USD/CHF | Major | Swissie |
| USA | Canada | USD/CAD | Major | Loonie |
| Australia | USA | AUD/USD | Major | Aussie |
| New Zealand | USA | NZD/USD | Major | Kiwi |
Here are some facts about major currency pairs:
- Major Pairs Are Very Liquid: lots of people trade them so their price changes fast meaning you spend less time in the market.
- Lower Volatility: price movement of major pairs is more predictable meaning they don’t suddenly jump to record highs/lows; they follow a pattern.
- Lower Fees: brokers charge lower fees when you trade major pairs because they are less volatile than others.
What Is A Minor Currency Pair?

The US Dollar is noticeably absent from all minor pairs & this is a trademark of minor pairs.
A minor currency pair is made up of two currencies of large economies excluding the United States.
Facts about minor currency pairs:
- Lower Liquidity: minor pairs are not as liquid as major currency pairs because the US Dollar, which is the most traded currency in the world, is absent.
- High Volatility: with the USD absent, major pairs can be unstable because most of the economies behind them are not as robust as the US economy.
- Slightly Higher Fees: with higher volatility comes higher fees & you see this in the form of wider spreads.
What are Exotic Currency Pairs?
The word exotic has to do with something rare & expensive. Exotic currency pairs are not traded frequently & attract high fees.
An exotic currency pair is one that contains a massively traded currency like the USD & a rarely traded currency like Norwegian Krone.
Examples of exotic currency pairs are:
- US Dollar vs South African Rand – USD/ZAR
- US Dollar vs Nigerian Naira – USD/NGN
- US Dollar vs Singaporean Dollar – USD/SGD
- Euro vs Norwegian Krone – EUR/NOK
- Euro vs Danish Krone – EUR/DKK
- US Dollar vs New Israeli Shekel – USD/ILS
Facts about exotic currency pairs:
- High Price (can be very unaffordable): exotic pairs have high prices or exchange rates, making thus them unaffordable to many.
- Poor Liquidity: not many people trade exotics, so their liquidity is poor causing their price to change slowly hence you spend more time trading them.
- Extreme Volatility: their price could jump up or down suddenly and in huge leaps causing you huge losses or profits.
- High Spreads: the volatile nature of exotics means you can make high profits so your broker charges higher spreads to get a piece of the action.
What is the Best Currency Pair in Forex?
The EUR/USD is the best currency pair to trade because its exchange rate or price is low, making it affordable so you see a lot of people trading it.
Because lots of people trade EUR/USD, you can open/close a trade quickly & at a good price, because there’s always a willing buyer or seller for your desired price.
The economies behind the EUR/USD pair are also very stable and their fiscal/monetary policies are solid. This means the EUR/USD exchange rate remains steady around 1.1000 level making it possible to plan long term trades.
When trading EUR/USD you will notice chart patterns form clearly, prices change regularly, fundamental analysis works properly, so you have a better trading experience.
There is also a lot of historical data for the EUR/USD making back testing possible, & a lot of automated trading bots have been developed around the EUR/USD.
How to Read Currency Pairs
There are two ways to trade: Long Trade or Short Trade.
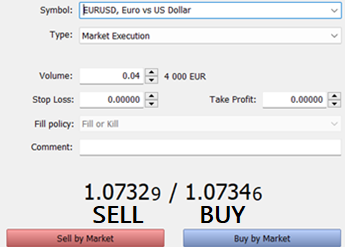
A forex price quote shows you how much you will pay to open both long & short trades.
The higher price is the buy price & the lower price is the sell price.
- To open a long trade, you pay the buy price
- To open a short trade, you pay the sell price
What is the difference between Bid/Ask and Sell/Buy price in Forex?
The Buy Price is another name for Ask price & The Sell Price is another name for the Bid price. On some forex apps the nomenclature is not Sell/Buy instead they call it Bid/Ask Price.
If a Bid/Ask price is quoted as 1.0732/1.0734 it means to enter a long trade, you pay 1.0734 and to enter a short trade you pay 1.0732.
Currency Pair Correlation
Correlation in forex means how the prices of two assets follow one another.
Correlation is one reason why you see forex traders looking at so many screens at the same time. They try to watch the behavior of all correlated pairs.
Correlation could ether be positive or negative.
Positive Correlation
Positively correlated currency pairs will rise together & fall together. This means their prices move in the same direction.
An example of positive correlation is the relationship between USD/CAD & Oil prices.
Because Canada depends on its crude oil sales to run most its economy, if the oil price falls the USD/CAD exchange rate will also fall.
Negative Correlation
Negatively correlated currency pair prices always move in opposite directions tp each other meaning when the price of one is up, the price of the other will be down.
An example of negative correlation is the relationship between the EUR/USD & U.S. Dollar Index (DXY).
The US Dollar Index (DXY) price rises when the USD is gaining strength while the EUR/USD price falls when the USD is also gaining strength.
So, there is a negative correlation between EUR/USD & DXY because when one rises, the other falls.
If you were trading the EUR/USD pair, it would be wise to monitor the DXY as well for confirmation of trends.

Leave a Reply